The seminal work of Canadian physiologist Hans Selye, the general adaptation syndrome (GAS) model, forms the basis of many discussions regarding the monitoring of physiological stress (100, 101). As outlined in chapter 1, the aim of training is to provide a stimulus that improves performance. Optimizing this relationship requires a solid understanding of the GAS. The model is based on the stages the body, or physiological system, goes through following some type of stimulus. In general, this model proposes that all stressors result in a similar response and that stress can be considered a disruption of the body’s homeostatic state.
Figure 3.1 outlines the GAS model. Upon the application of a stimulus or stress, the body enters the shock or alarm phase, which results in training fatigue. Acute fatigue is a normal and expected short-term response to the training stress and an important part of the training process. If adequate recovery follows this initial stress, the second phase, known as the resistance phase, occurs, in which the system returns to baseline, or homeostasis. It is during this return to homeostasis that physiological adaptations are made. This ensures that the training stimulus applied in the future does not disrupt the athlete to the same degree (43). For the third phase, known as supercompensation, to occur, an adequate recovery period must follow the training stimulus. Supercompensation refers to a return to a level that exceeds the baseline, resulting in an increased performance capacity. To ensure optimal training adaptations and benefits, the next training stimulus must be imposed during the supercompensation phase. Insufficient recovery can lead to a final phase characterized by decreased performance and eventually overtraining.
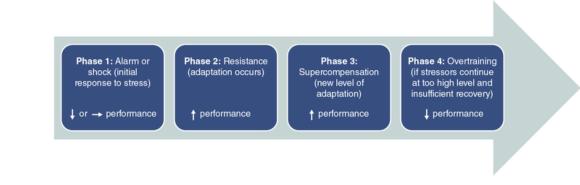
Model of the general adaptation syndrome.
Although the GAS model does not cover all aspects of the response to stress, it is useful for explaining the adaptive response to an acute training stimulus. It is worthwhile noting that the GAS model is not a linear response. All athletes experience fluctuations within days, between days, and across microcycles (generally 7-10 days).
Problems can arise in the GAS when a secondary training stimulus is applied too early. The result can be excessive fatigue, which can lead to training maladaptations. This could eventually result in decreased performance and, in severe cases, negative consequences such as overtraining as depicted by phase 4 in figure 3.1. Alternatively, if no secondary training stimulus is applied during the supercompensation phase, any training adaptations may be lost as the athlete returns to pretraining homeostasis levels.
The delicate balance between overload and underload is extremely important for practitioners to manage. An effective athlete monitoring system can inform the practitioner about the training fatigue and adaptations occurring in athletes. Although the GAS model is a simple representation of how training adaptations occur, it provides a good starting point for understanding the effect of acute training stimuli. The problem with oversimplification, though, is that it can cause practitioners to miss several key aspects in their understanding of athlete monitoring. The reality is that the effect of training dosage on training adaptation is very complex. A wide range of factors and interactions occur during training that make it difficult to analyze the training adaptation response. Practitioners must keep in mind that the impacts of stressors are additive and that other factors can affect the athlete’s ability to respond and adapt to the stressors that result from the training (5, 66). Traditional concepts of homeostasis need to take into account the multifactorial nature of athlete training. Specifically, practitioners need to understand how athletes perceive the stress and how their training histories affect how they cope with it.
Save